The Vedic Age
The History of Vedic India is known largely through its religion text, the Vedas, which gave the period its name. The Vedas recorded not only the religion of the Vedic people, but also details of their lives that give us glimpse of there political, social and Economical life.
The Aryans
- There are Many Theories about the origin of Aryans. The most accepted view that they lived in great steppe land which stretches from Poland to Central Asia. They were semi-nomadic People .
- The Boghaz Kai inscription dated 1400 BC gives the information about peace treaty between the Hittites and Mittanis ruler of Hittani, in which names of the Vedic Gods Indra, Mitra, Nasatya and Varuna are mention. This supports view of central Asian homeland theory that the central Asia was Aryan homeland.
- The Aryans means Noble people.
- They Speak Sanskrit and Indio-European language.
Vedic Age was Divided into two Parts, which are as follows:
i. Early Vedic Age from 1500 BC- 1000 BC
ii. Latter Vedic Age from 1000 BC-600 BC
Early Vedic Age (1500 BC- 1000 BC)
The main source of information for study of early Vedic age people is the Rigveda. The founder of Vedic culture, were the Aryans, probably immigrant people whose first arrival in India is dated around 2000-1500 BC.
The Rig Vedic Age
- They have Monarchical system.
- The Rig Veda gives as information that the Aryans first settled at the region called Sapta Sindhu or the land of the seven rivers (Presently that is region is- East Afghanistan, Punjab and West UP)-Indus, Jhelum, Ravi, Chenab, Beas, sutlej and Saraswati. Sarswati was most pious river.
- Early Aryans were semi-nomadic and latter on, they became cultivator. They Gave Great preference to the cattle, so the ruling class was warrior who were able to fight for cattle.
The Rig Vedic Society
- The Rig Vedic society was base on kinship. The early Aryans were essentially tribal and egalitarians.
- Tribe Was Called Jana. The basic unit of society was family of graham. The head of family is known as Grihapati.
- There is No Child marriage concept.
- Women's enjoy respectable position. They allowed to take part in Shabha And Samiti.
- There is womens poets also Apla, Lopamudra, Viswavara and Ghosha.
- Society was patriarchal, generally monogamy was practiced while polygamy was prevalent to royal and nobles families.
- Existence of joint family pattern, were women given equal opportunities as men their spiritual and intellectual development. Eldest male member of the family was known as Kulapa.
The Rig Vedic Religion
- The early Vedic people were nature worship. neither they had temple nor idols. They worship by means of recitation of mantra.
- The motive of worship was to get Praja (Children), Pasu (Cattle) Dhana (wealth), till that time they don't required spiritual upliftment.
- Boghazkai inscription of 1400 BC found in Asia Minor (Turkey) has mention a four god Indra, Mitra, Varuna, Nasatya.
The Varna System
The Varna system in Dharma-shastras divides society into four varnas (Brahmins, Kshatriyas, Vaishya and Shudras). Those who fall out of this system because of their grievous sins are ostracised as outcastes (untouchables) and considered outside the varna system.
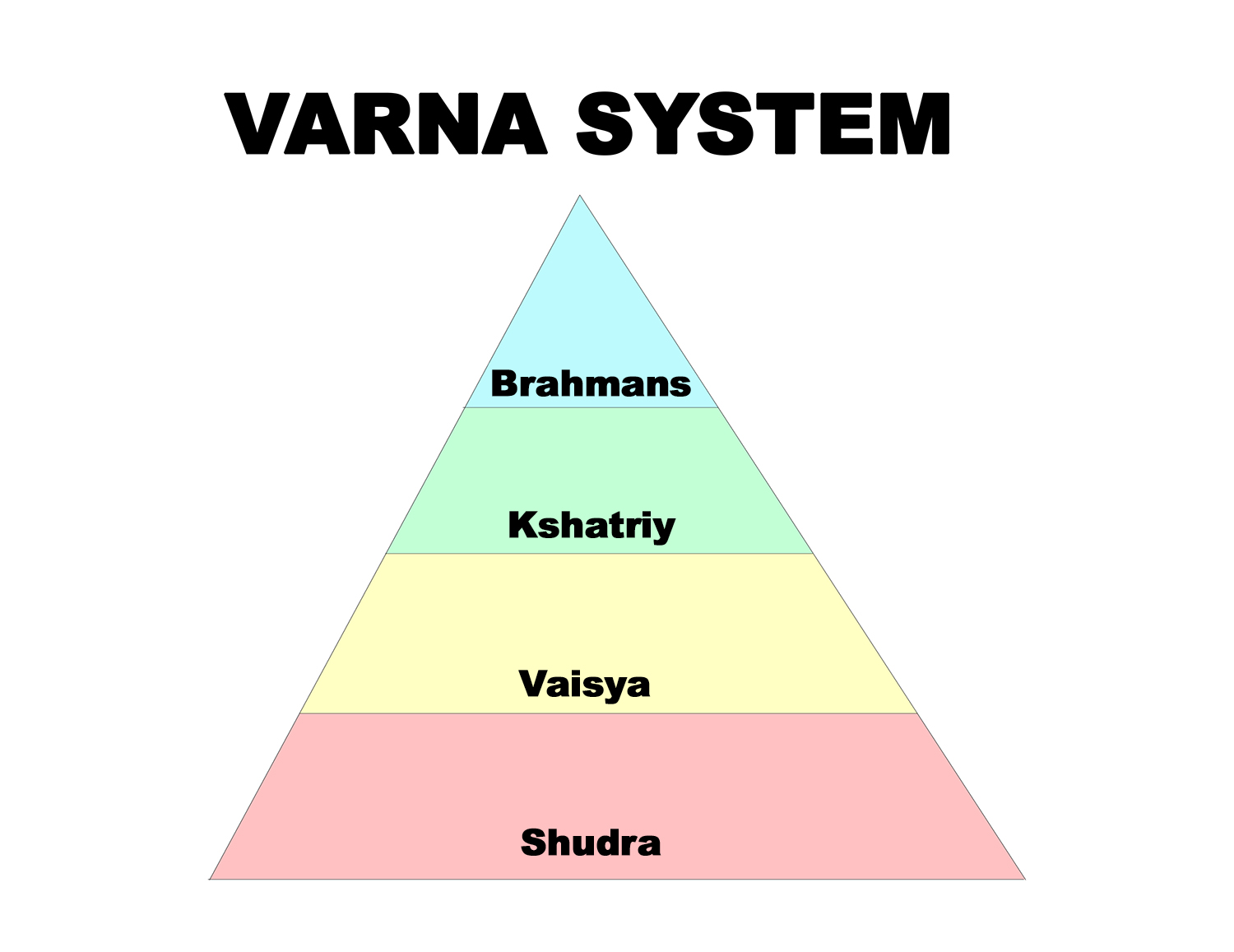

- Brahmans: Vedic scholars, priests and teachers.
- Kshatriya: rulers, warriors and administrators.
- Vaishya: agriculturalists and merchants.
- Shudras: laborers and service providers/servant.
Gods
- Goddess Usha- Goddess of Dawn, Aditi - Mother of Gods, Prithvi - Earth Goddess, Aryani - The forest Goddess.
- Indra 250 hymns of Rig Veda are dedicted to Indra. He was also known as Purandhar on the destroyer of the forts. He was also worshiped as 'God of War'.
- Varuna He was upholder of Rita or cosmic order of regulated it by dice. It was believed that whatever is happening in the world is/was related with desire of God Varuna.
- Agni He was second most important God. About 200 hymns in Rig Veda were attribute to Agni. Agni was called intermediary God between God and Man.
- Soma God of Plants. special hymns given to Soma (9th mandala of Rig Veda is dedcated to Soma).
- Dyaus Father of Indra. (Dyases means Heaven).
- Ashwin Healer of wounds and surgeon.
- Surya and Savitri (the God of light) was Solar God. The Gyatri mantra is addressed to the Savitri in 3rd mandala of Rig Veda, which was composed bu maharishi Vishwamitra.
- Pusan Guardian of roads, herdsman and cattle.


